What is the PERT model?
PERT is an acronym for Program Evaluation Review Technique and is a visual project planning method. It helps you to plan the average duration of certain tasks over the course of the project. This allows you to better estimate the expected overall project timeline and cost.

PERT was developed by the US Navy in 1958 to simplify the planning of the complex Polaris missile submarine project. The research and production of new components for the submarine were distributed to various contractors. It wasn’t possible to calculate the exact time and effort required for the individual steps, which is why the contractors were asked to provide an estimate of the possible duration.
At the same time, the private sector developed the critical path method (CPM). This method is similar to PERT. Both visually represent the project timeline. The only difference is that the CPM works with the longest estimated task duration of project tasks. PERT, on the other hand, works with 3 different task duration estimates:

PERT is, therefore, a more differentiated approach than the critical path method.
The PERT model was also used in the organization of the 1968 Grenoble Winter Olympics. Although numerous similar management concepts have been devised and developed since then, PERT was the first technique of its kind – and it’s still popular today.
What is a PERT chart?
A PERT chart is the practical application of the PERT model. It helps you to visualize the planned tasks of a project and their dependencies. For example, it’s useful if you want to share an initial timeline and a projected schedule with stakeholders before the project launch.
Discover the PERT Chart Template by MindMeister Public Maps. Tailor this PERT chart template to your project and link out to it from your MeisterTask overview task.
How do PERT charts improve your projects?
As a project manager, a PERT chart helps you to visually plan a project in a structured way – and execute it methodically. Use a PERT chart to easily evaluate the schedule, the necessary resources and the critical path of your project. Doing so will…
Improve your time management. A PERT chart highlights both the individual task duration and the overall project duration. It’s a great method to define the expected schedule in detail during the project planning phase.
Improve your resource management. With a PERT chart, you can easily see which tasks require which resources. This saves you and everyone involved in the project time, as everyone can easily access the information independently.
Improve your project overview. One of the key features of a PERT chart that sets it apart from other methods is its ability to determine the critical path of a project. The critical path method is important if you want to visualize the schedule of your project with all of its task dependencies and uncertainties.
When should you use a PERT chart?
As mentioned above, PERT was developed for planning extremely complex projects. In other words, projects in which you and your team must coordinate and work through many parallel and consecutive tasks.
If your project requires allocating multiple tasks to various team members, a PERT chart can help. This practical template provides a robust framework that can serve as a basis for further steps.
However, to implement the PERT model, you also need reliably observed data from the past or clear expert estimates of future expectations. If you do not have this data, the results will not be accurate or helpful.
If you’re dealing with a fairly straightforward project, introducing the PERT model will only cause confusion. Valuable time will be wasted on estimations, which are unnecessary due to the lack of detail in the project. Note that there are disadvantages to PERT charts, including:
Calculating PERT and creating a chart is time-consuming. Once you start subdividing all the necessary tasks, the number of tasks to manage can quickly become overwhelming.
You need to create a PERT chart before the launch of your project for the administrative effort to be worth it.
If the optimistic and pessimistic estimates deviate greatly from the probable value, you’ll end up with a distorted result, which can ultimately lead to bad decisions.
It’s difficult to give a concrete indication of the project duration, even with expert input.
Diagrams such as PERT charts help illustrate expectations – but not the project status.
Expectations are not necessarily met during the project, which can quickly make your PERT chart redundant.
How to create a PERT chart and integrate it into your project
To create a PERT chart and integrate it into your project seamlessly, complete the following 6 steps in order:

1. Identify all project tasks
To create a successful PERT chart, start by identifying and collecting all project information and tasks. Use either a mind map or a note in your task management tool.
Not using a digital task management tool? Find out why you should and how it benefits your team.
Whichever you choose, share it with your team and work on it collaboratively to quickly gather more insights. More eyes on it means less chance anything will be forgotten.
2. Define all task dependencies
You should now identify all tasks that rely on the completion of another task to be worked on.
Identifying all task dependencies will help you to:
Allocate tasks appropriately and follow up on them later.
Ensure the timely completion of tasks.
Make clear what needs to be communicated, when and to whom.
3. Open your PERT chart template
The best way to create a PERT chart is to open the MindMeister template (shown under “What is a PERT chart?”) and transfer the final tasks and dependencies in a logical sequence into your task management tool.
To make this easier, number the tasks and add the responsible person to your list before you transfer the information over.
4. Estimate the duration of each project task
Now it’s time to plan your project timeline by applying the PERT formula to each of your tasks:

You use the formula to calculate the average value from the three estimated values for each task, with the most probable cause being weighted by a factor of 4. This results in the planned value, also known as the PERT value.
This calculation relies on previous experience and data. It helps you to communicate with your project team – in the best case directly in your MeisterTask tasks – how long a task will realistically take.
With PERT, you usually calculate back from a fixed end date rather than the other way around, as contractor deadlines often cannot be moved.
PERT example: calculation using the PERT formula
Let’s assume that the marketing team at AllGood GmbH needs a visualization of the collected campaign data.
The team knows from experience that under optimal conditions, when all the information is available, they require 300 minutes to do this. Under normal conditions, when only individual pieces of information need to be researched, it takes 450 minutes. Under unfavorable conditions, when missing documents have to be requested, 600 minutes. The planned values are calculated using the PERT formula as follows:
Planned value = (300 + (4 × 450) + 600) / 6 = 2700 / 6 = 450 minutes = 7.5 hours
5. Create all tasks in your task management tool
Create all the main or “parent tasks” for your project in your task management tool. Define the person responsible for the task, add all project participants as watchers, and link out to your project overview note and PERT diagram.
It’s likely your task requires contributions from multiple team members. To provide more clarity as to what needs to be done and when, break down your high-level tasks into subtasks. Assign them to the responsible person with the required due date. However, keep discussions to the parent task. This will ensure that your team uses this project task as the single source of truth for the project – and they don’t miss any updates.
6. Coordinate your project workflows
Now all that remains is to coordinate the delivery of the tasks until the project is complete. By centralizing all your communication in your parent project task – where you can also access the linked PERT diagram at any time – you and your team can easily track the progress of each task and communicate updates.
Subscribe to our blog
Get the latest articles in your inbox
You can find out more about how we handle personal data in our Privacy Policy.
How does a PERT chart differ from a GANTT chart and CPM chart?
All three charts have a common purpose: to improve project planning. But there are a few key differences between them.
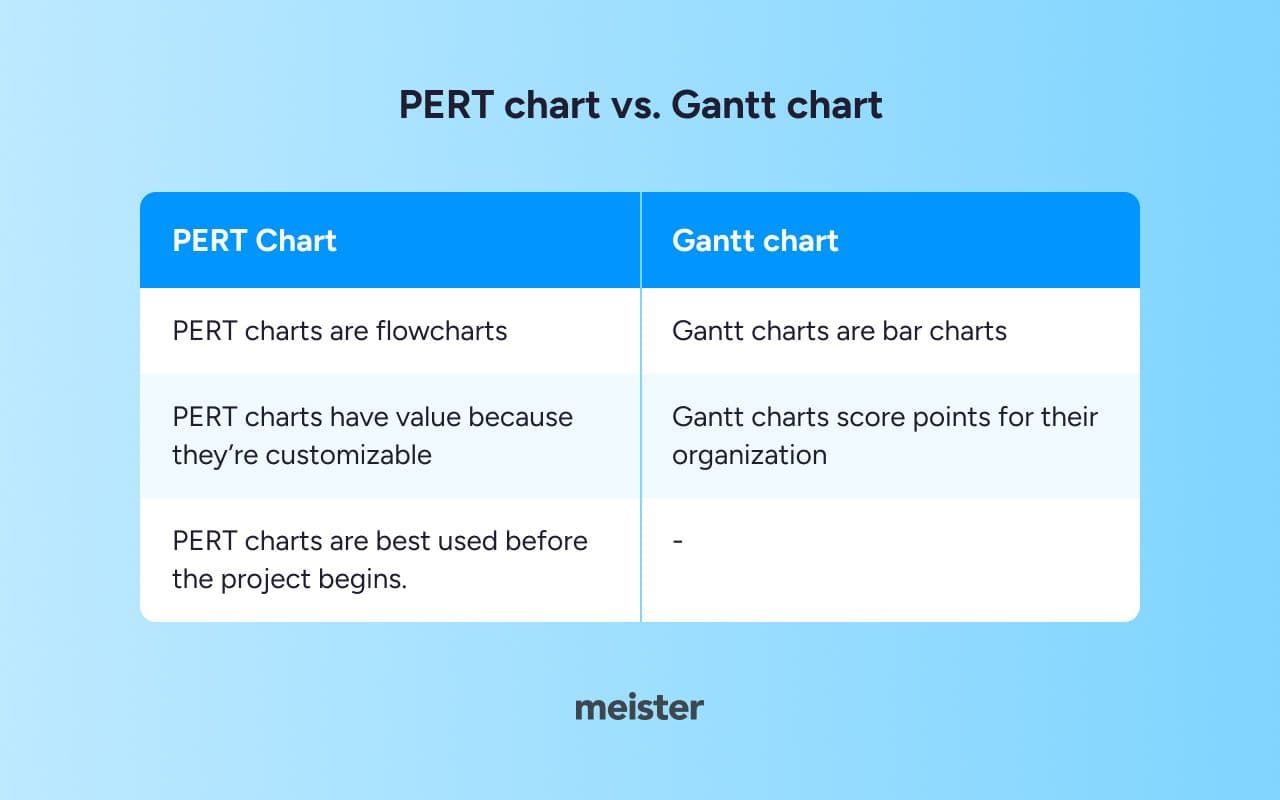
PERT chart vs. Gantt chart
PERT and Gantt charts are often conflated, but there are important differences between them. Not only do they differ visually, but they also offer different functions to suit different needs.
PERT charts are flowcharts, Gantt charts are bar charts. The former are less structured in their appearance and the layout can be slightly different depending on the project.
Gantt charts score points for their organization, but PERT charts have value because they’re customizable. Gantt charts offer an organized structure while PERT charts allow for easy layout customization, which is better suited for presenting top-level project plans.
PERT charts are best used before the project begins. With their simple timeline-friendly layout, PERT charts are typically used as visual aids during a project kick-off. Project managers then like to use other methods, such as a work breakdown structure, a GANTT diagram or a Kanban board, to specifically assign project tasks and highlight dependencies.
Ultimately, GANTT charts are best suited for mapping project tasks throughout the project cycle, while PERT charts are best used for planning and scheduling in the initial project phase. The charts can be used separately or together to create a comprehensive project plan.
PERT chart vs. CPM chart
Both charts, i.e. PERT and CPM charts, are models for project planning and management. They’re used to efficiently plan and organize task sequences for larger projects.
The main difference is that project managers like to use PERT charts to determine how much time will be required to complete a project, while they use CPM charts to control costs and time spent.
For optimal results, you can use CPM charts in parallel with PERT charts. By integrating both methods into your project management strategy, you can give your team a realistic deadline and provide the optimal workflow for your project.
Get productive with PERT
Sounds interesting? Then give it a try. Your PERT template is waiting for you! For further suggestions and tips on project planning, refer to the MeisterTask Community.


